Description
There is a double row outer ring (double raceway outer ring) and two inner rings with rollers and cage components (cones), usually with a spacer between the two inner rings 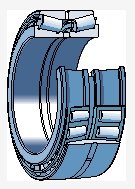
There are several rows of rollers arranged back-to-back (with the load line separated from the axis of the bearing) to provide a highly rigid bearing arrangement and withstand significant overturning moments
It is a quick installation unit with preset axial clearance or preload during manufacturing
Can be used as a positioning end bearing or a floating end bearing:
For floating end bearings, axial displacement should occur between the outer ring and the bearing seat hole
Bearings with blind holes or positioning grooves on the outer ring can be fitted with cylindrical pins to prevent the outer ring from rotating on its base
IMCB has manufactured various types (types/characteristics) of TDO type bearings, such as:
Design form characteristics
TDO
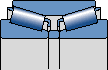
There is a spacer between the two inner rings
Window steel retaining frame
TDO.1
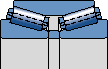
There is a spacer between the two inner rings
Pillar type steel cage (perforated roller) suitable for higher loads
TDON
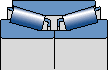
No spacer ring
The interdependent inner circle
Window steel retaining frame
TDO/Z
There is a spacer between the two inner rings
Window steel retaining frame
Steel plate dust covers on both sides
TDOS.1
Large contact angle α
Suitable for applications where high axial loads or high overturning moments occur together with radial loads
There is a spacer between the two inner rings
Pillar type steel cage (perforated roller) suitable for higher loads
TDI type bearings
There are two outer rings (cup-shaped) and a double row inner ring with two rollers and a cage assembly (double cone), usually with a spacer between the two outer rings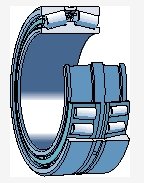
There are several rows of rollers arranged face to face (load lines converge towards the axis of the bearing)
Open or with dust cover or seal
Both sides are equipped with HNBR or FKM contact seals
It is a quick installation unit with preset axial clearance or preload during manufacturing
Mainly designed for use as a fixed end bearing
Optional holes with spiral grooves and/or lubrication grooves on the side of the bearing ring 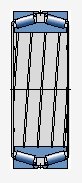
When loose fit is required on the shaft, these slots will compensate for the disadvantage of loose fit
When the inner ring rotates under load on its support, these grease lubricated grooves can supply lubricant between the inner ring and the support surface
In addition, these grooves can also absorb wear particles
IMCB has manufactured various types (types/characteristics) of TDI type bearings, such as:
Design form characteristics
TDI
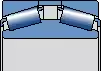
The spacer between two outer rings
Window steel retaining frame
TDI.1
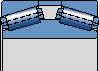
The spacer between two outer rings
Pillar type steel cage (perforated roller) suitable for higher loads
TDIE
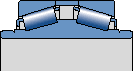
The spacer between two outer rings
Window steel retaining frame
Extend the inner circle at both ends
The extended part has been ground to serve as the mating end face for the sealing lip
TDIT
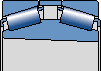
The spacer between two outer rings
Conical hole, taper 1:12
Window steel retaining frame
TDIS
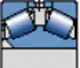
Large contact angle α
Suitable for applications where high axial and radial loads occur simultaneously
The spacer between two outer rings
Window steel retaining frame
Used in rolling mill applications with loose fit on the roll neck, and only capable of bearing pure axial loads
There are one or more positioning slots (grooves) on one or both sides of the inner ring to prevent it from rotating on the base
Depending on the purpose, the bearing can have or not have a spacer between the two outer rings
TDIS.1
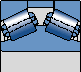
Large contact angle α
Suitable for applications where high axial and radial loads occur simultaneously
The spacer between two outer rings
Pillar type steel cage (perforated roller) suitable for higher loads
TDIS.2
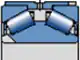
There is a self holding unit with a retaining sleeve on the outer ring
The outer ring is pressed into the liner
The deformation of the outer ring caused by axial overload is significantly improved
Therefore, the pressure distribution in rolling contact is more favorable, thereby extending the service life of the bearing
The axial internal clearance depends on the sleeve
No need to preload with springs
Large contact angle α
Suitable for applications where high axial and radial loads occur simultaneously
Simplified and economical design facilitates installation, disassembly, and maintenance inspection procedures





